What are PCOS and PCOD and Difference between These Two
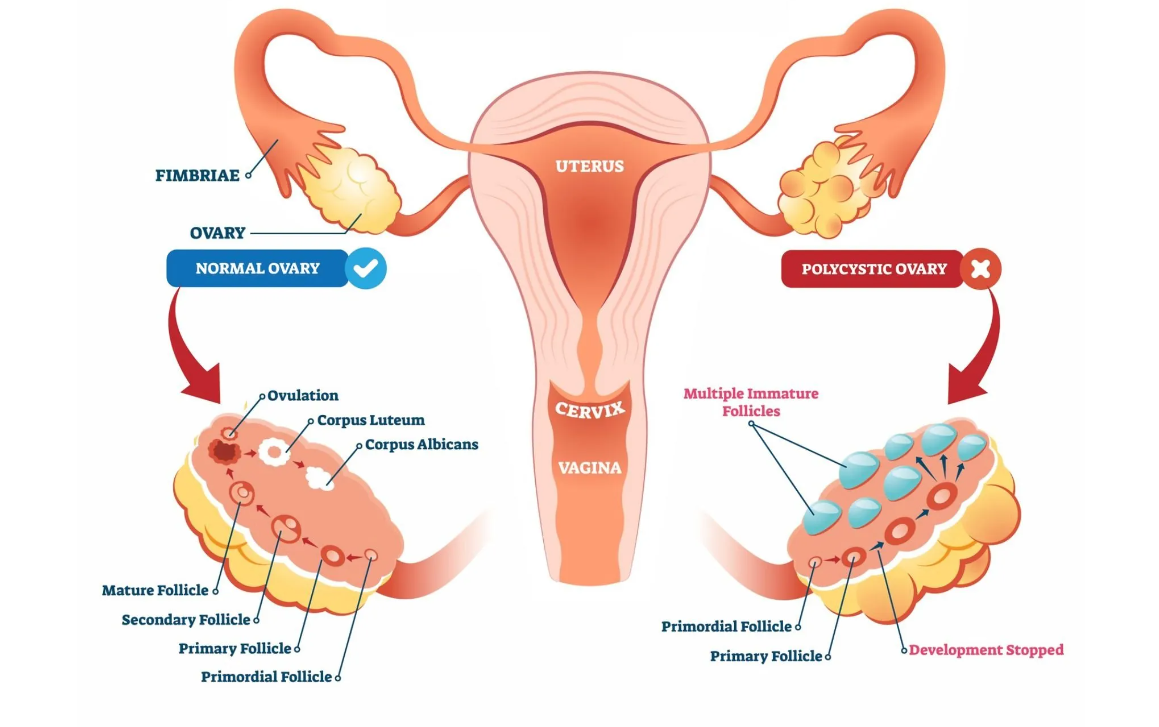
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) are conditions that impact women's reproductive systems. Whereas the two terms are frequently used interchangeably, they are not the same.
What is PCOD?
PCOD or Polycystic Ovarian Disease is a hormonal imbalance in a woman's body. When a woman with the disease ovulates, her ovaries release immature eggs. As a result, immature eggs gather in the ovaries, resulting in cysts.
The cysts enlarge the ovaries, causing them to secrete more male hormone androgen, which disrupts the menstrual cycle. Hair loss, unusual weight gain, facial acne, and hair growth are all symptoms of PCOD. Some women may also be infertile.
Excess insulin release in the body, obesity, stress, hormonal disruptions, and lifestyle issues are all factors that contribute to PCOD.
PCOD or Polycystic Ovarian Disease is a hormonal imbalance in a woman's body. When a woman with the disease ovulates, her ovaries release immature eggs. As a result, immature eggs gather in the ovaries, resulting in cysts.
The cysts enlarge the ovaries, causing them to secrete more male hormone androgen, which disrupts the menstrual cycle. Hair loss, unusual weight gain, facial acne, and hair growth are all symptoms of PCOD. Some women may also be infertile.
Excess insulin release in the body, obesity, stress, hormonal disruptions, and lifestyle issues are all factors that contribute to PCOD.
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is a hormonal disorder in which the ovaries of a woman produce excessive amounts of testosterone, a male hormone. This hormone interferes with the formation and release of female eggs, resulting in ovarian cysts. This results in irregular menstrual cycles and infertility issues in women. Obesity, anxiety, acne, pelvic pain, infertility, miscarriage, and other symptoms of PCOS may occur in women.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome has no known cause. However, insulin resistance may cause a woman's body to produce more male hormones. Furthermore, PCOS has a genetic component. PCOS can result in irregular periods, weight gain, acne, excessive hair growth, and infertility.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is a hormonal disorder in which the ovaries of a woman produce excessive amounts of testosterone, a male hormone. This hormone interferes with the formation and release of female eggs, resulting in ovarian cysts. This results in irregular menstrual cycles and infertility issues in women. Obesity, anxiety, acne, pelvic pain, infertility, miscarriage, and other symptoms of PCOS may occur in women.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome has no known cause. However, insulin resistance may cause a woman's body to produce more male hormones. Furthermore, PCOS has a genetic component. PCOS can result in irregular periods, weight gain, acne, excessive hair growth, and infertility.
What is the Difference Between PCOD and PCOS?
PCOD is a metabolic condition that is caused by lifestyle factors, whereas PCOS is an endocrine condition caused by hormonal imbalance. Meanwhile, the reason for the hormonal imbalance in PCOS is unidentified.
PCOD is more prevalent than PCOS. PCOD affects approximately 10% of women worldwide, whereas PCOS affects fewer women.
PCOD can be cured by making changes to one's lifestyle and eating habits. However, PCOS is a complex medical condition that, if not treated early on, is fatal.
Women with PCOS may develop medical issues such as diabetes, cardiac vascular conditions, high blood pressure, and so on, whereas women with PCOD do not.
Women with PCOD do not have fertility problems, but in most cases, PCOS leads to infertility or miscarriage.
PCOD is a metabolic condition that is caused by lifestyle factors, whereas PCOS is an endocrine condition caused by hormonal imbalance. Meanwhile, the reason for the hormonal imbalance in PCOS is unidentified.
PCOD is more prevalent than PCOS. PCOD affects approximately 10% of women worldwide, whereas PCOS affects fewer women.
PCOD can be cured by making changes to one's lifestyle and eating habits. However, PCOS is a complex medical condition that, if not treated early on, is fatal.
Women with PCOS may develop medical issues such as diabetes, cardiac vascular conditions, high blood pressure, and so on, whereas women with PCOD do not.
Women with PCOD do not have fertility problems, but in most cases, PCOS leads to infertility or miscarriage.
Signs and Symptoms of PCOD and PCOS:
Signs and Symptoms of PCOS: Here are the symptoms of PCOS –
Signs and Symptoms of PCOS: Here are the symptoms of PCOS –
- Periods that are irregular
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Male pattern hair loss
- Hirsutism
- Headaches
- Acne
- Skin discoloration in areas such as the armpits, neck, and groin
- Gaining weight
- Oligomenorrhea (less than nine menstrual periods in a year)
- Amenorrhea (absence of menstrual periods for three months or more)
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
What Causes PCOD and PCOS:
PCOD: It is thought to be connected to the following:
PCOD: It is thought to be connected to the following:
- Sedentary way of life
- A diet that is unhealthy
- Hormone replacement medication
- Pollution
- Insulin overproduction
- Inflammation
- Rise in androgen Level
- Insulin sensitivity
- Excessive levels of androgen
- Low-level inflammation
- Heredity
Diagnosis of PCOD and PCOS:
The doctor may recommend a pelvic examination through physical examination, blood tests to examine hormonal disturbances, and pelvic ultrasound to diagnose both PCOD and PCOS diseases.
The doctor may recommend a pelvic examination through physical examination, blood tests to examine hormonal disturbances, and pelvic ultrasound to diagnose both PCOD and PCOS diseases.
PCOD and PCOS Treatment:
Treatment for PCOD problems and PCOS complications includes treatment for various PCOS vs PCOD symptoms that aid in hormonal balance or irregular menstrual cycles.
Hair Treatment: PCOS and PCOD can cause an increase in androgens, or male hormones, due to hormonal imbalance. In women, this will result in excessive hair growth on the face. Oral contraceptives are used to treat hair growth and hair loss.
In women with bilateral polycystic ovary syndrome and PCOD, these medications will suppress male hormone production. Special creams, such as eflornithine cream, are available to remove unwanted facial hair. Waxing, plucking, shaving, threading, or laser hair removal treatments are also options for painless and permanent hair removal.
Surgery: Ovarian drilling is a type of laparoscopic surgery used to remove cysts in the ovaries which produce male hormones in women. Laparoscopy is recommended to treat fertility problems in women who do not respond to medication. In the case of cancerous cysts or endometrial cancer, a hysterectomy is recommended.
Medications: While there are various medications available to treat the common signs and symptoms of PCOS or to prevent future PCOD problems, there is no complete treatment for this condition.
Fertility treatment: IVF (In vitro fertilization) and artificial insemination are fertility treatments for females with PCOS or PCOD. In the lab, the egg is fertilized with sperm before being transferred to the mother's womb for implantation. If medications and surgery do not work, this is the last and best option for treating PCOD or polycystic ovary syndrome.
Treatment for PCOD problems and PCOS complications includes treatment for various PCOS vs PCOD symptoms that aid in hormonal balance or irregular menstrual cycles.
Hair Treatment: PCOS and PCOD can cause an increase in androgens, or male hormones, due to hormonal imbalance. In women, this will result in excessive hair growth on the face. Oral contraceptives are used to treat hair growth and hair loss.
In women with bilateral polycystic ovary syndrome and PCOD, these medications will suppress male hormone production. Special creams, such as eflornithine cream, are available to remove unwanted facial hair. Waxing, plucking, shaving, threading, or laser hair removal treatments are also options for painless and permanent hair removal.
Surgery: Ovarian drilling is a type of laparoscopic surgery used to remove cysts in the ovaries which produce male hormones in women. Laparoscopy is recommended to treat fertility problems in women who do not respond to medication. In the case of cancerous cysts or endometrial cancer, a hysterectomy is recommended.
Medications: While there are various medications available to treat the common signs and symptoms of PCOS or to prevent future PCOD problems, there is no complete treatment for this condition.
Fertility treatment: IVF (In vitro fertilization) and artificial insemination are fertility treatments for females with PCOS or PCOD. In the lab, the egg is fertilized with sperm before being transferred to the mother's womb for implantation. If medications and surgery do not work, this is the last and best option for treating PCOD or polycystic ovary syndrome.
What are PCOS and PCOD and Difference between These Two PCOS PCOD Polycystic Ovarian Disease Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome hormonal disorder Difference Between PCOD and PCOS Signs and Symptoms of PCOD and PCOS
Comments